Google’s custom Tensor chips, introduced with the Pixel 6, have aimed to bring distinct features to its devices, though they’ve often fallen short on performance and efficiency compared to other leading processors. However, recent leaks reveal that Google’s upcoming Tensor G6 chip, codenamed “Malibu,” may shift priorities toward efficiency over performance, a move that could still bring meaningful benefits to Pixel users.
According to leaked internal documents reported by Android Authority, the Tensor G6 won’t make substantial performance gains over its predecessors. Instead, Google is focusing on improving thermal efficiency and chip size, potentially making the G6 better suited for users who prioritize battery life and consistent performance without overheating.
Google’s Chip Strategy: Prioritizing Efficiency Over Performance
The Tensor G6 will follow Google’s recent trend of modest performance increases; the previous generation, Tensor G5, is also expected to offer only minor improvements over the current G3. This decision to focus on efficiency rather than raw power may seem like a step back for some, but it aligns with Google’s goal of refining the Pixel experience through software and optimization rather than simply increasing processing speed.

Why Google May Use the Tensor G4 GPU in the G6
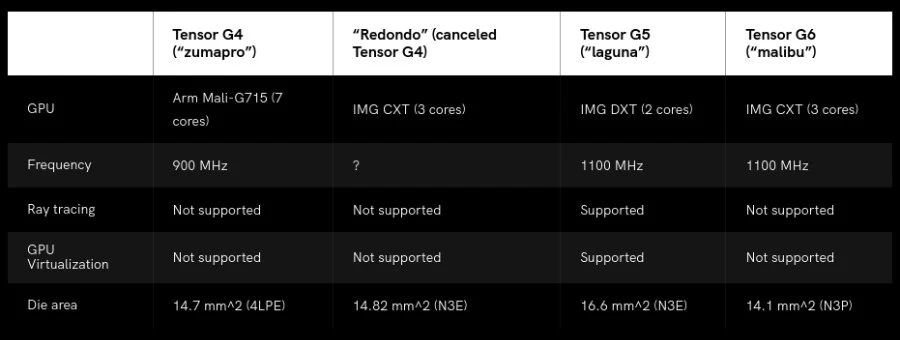
One noteworthy element of the Tensor G6 is the potential reuse of the GPU design originally intended for the Tensor G4. Instead of introducing a new GPU with advanced features like ray tracing, Google may use the G4’s GPU, which lacks this capability. While this may seem like a downgrade, it could actually benefit users by helping Google meet its design goals.
This decision appears to be motivated by Google’s desire to reduce the overall size of the chip, a crucial factor in enhancing efficiency and minimizing heat production. According to the report, the Tensor G6 will be manufactured using TSMC’s latest N3P process node, which offers a 4% reduction in chip area compared to the N3E process used for the G5. Google’s choice to reuse the G4’s GPU could result in a smaller, more efficient processor, bringing advantages in battery life and thermal management.
Managing Chip Size and Efficiency: Google’s Approach
In its push for a smaller chip, Google reportedly aims to reduce the Tensor G6’s die size to around 105 mm²—significantly smaller than the 121 mm² Tensor G5 chip. For comparison, Apple’s A18 Pro, which also uses TSMC’s 3nm process, measures around 105 mm², demonstrating that a smaller chip size is possible even with advanced technology.
Google’s reported strategy involves several design adjustments beyond the GPU. One major change is reducing the DSP (digital signal processor) by one core. Additionally, the system-level cache (SLC) will be halved from 8MB to 4MB, helping to further decrease the chip’s die area. These reductions in size may not bring significant speed improvements but could result in a more efficient, longer-lasting chip overall.
Why a Smaller Chip Could Be Good for Users
For Pixel users, Google’s strategy of prioritizing efficiency and thermal management could translate into a better real-world experience. Smaller, more efficient chips generate less heat and can potentially extend battery life by drawing less power, especially under intensive tasks. While this approach may not appeal to users who prioritize gaming or high-performance applications, it aligns well with Google’s focus on optimizing the Pixel experience for everyday usage.
By potentially reusing the G4 GPU, Google may sacrifice advanced features like ray tracing, which is popular in high-end mobile gaming, but it’s worth noting that the Pixel’s primary audience may not place as much emphasis on these features. Instead, Google appears to be doubling down on creating a balanced device that offers smooth performance, reliable battery life, and efficient power usage—all qualities that contribute to a user-friendly smartphone.
Balancing Cost and Performance in the Chip Market
Google’s decision to focus on efficiency and cost-saving measures reflects a broader trend in the chip industry, where brands are balancing performance gains with manageable production costs. The Pixel series’ unique appeal lies in its integration of Google’s software expertise with hardware, and the Tensor line has been a key part of that strategy, supporting Google’s advancements in AI and machine learning.
By keeping the Tensor G6 design relatively modest, Google can focus on optimizing the device’s software-hardware integration, allowing features like advanced AI-driven photography and real-time language translation to shine. This balanced approach, rather than a purely performance-focused upgrade, could make the Pixel series more accessible to a broader audience by keeping device costs competitive.
What Users Can Expect from the Tensor G6
While official specs are still under wraps, Google’s rumored approach with the Tensor G6 suggests that users may see improvements in battery efficiency and heat management rather than breakthrough performance. By leveraging a smaller GPU and reducing other components like the DSP and SLC, Google is betting that an optimized, space-saving design will ultimately result in a smoother and more dependable experience for day-to-day tasks.
These adjustments could make the Tensor G6 particularly suitable for users who use their devices for productivity, photography, and other standard applications rather than intensive gaming or professional-grade tasks. The smaller chip size could also contribute to slimmer device designs, adding to the Pixel’s portability and comfort in hand.
What This Means for Google’s SoC Development
The decision to prioritize efficiency in the Tensor G6 signals that Google may be refining its approach to custom chip design, focusing on optimizing the user experience rather than directly competing in the high-performance SoC market. As mobile technology continues to evolve, there’s a growing demand for devices that not only perform well but also manage power and heat effectively—qualities that benefit from smaller, more efficient processors.
If successful, Google’s Tensor G6 could mark a turning point in its custom chip strategy, positioning future Pixel models as smart, efficient devices tailored to the everyday needs of their users. And while the performance might not reach flagship levels, Google’s focus on software and efficiency could help the Pixel series carve out a distinct identity in a crowded smartphone market.
In conclusion, Google’s choice to use an older GPU design in the Tensor G6 may seem surprising at first, but it reflects a deliberate strategy to enhance efficiency, reduce chip size, and provide a more consistent user experience. As Google continues to refine its Tensor lineup, the G6 could serve as a compelling option for users who value reliability, battery life, and Google’s unique software experience over raw power. For Pixel fans, this focus on balanced performance and efficient design could make the Tensor G6 one of Google’s most refined chips yet, offering a device that’s not only smart but also built to last.
via




